:
About Puncture Vine:
Tribulus Terrestris seems to be an annual plant in the caltrop group (Zygophyllaceae) that is evolved to flourish in arid climatic settings where few other vegetation can survive. Goat’s-head, bindii, bullhead, Burra gokhru, bhakhdi, caltrop, little caltrops, cat’s-head, devil’s eyelashes, devil’s-thorn, devil’s-weed, pierce vine, and tackweed are all common names for this plant.
It is endemic to the Old World’s mild temperate and tropical areas, including southern Europe, southern Asia, Africa, as well as Australia. It may grow in arid areas and poor soil.
How to Spot Puncture Vine (a.k.a. the Goat Head Monster)
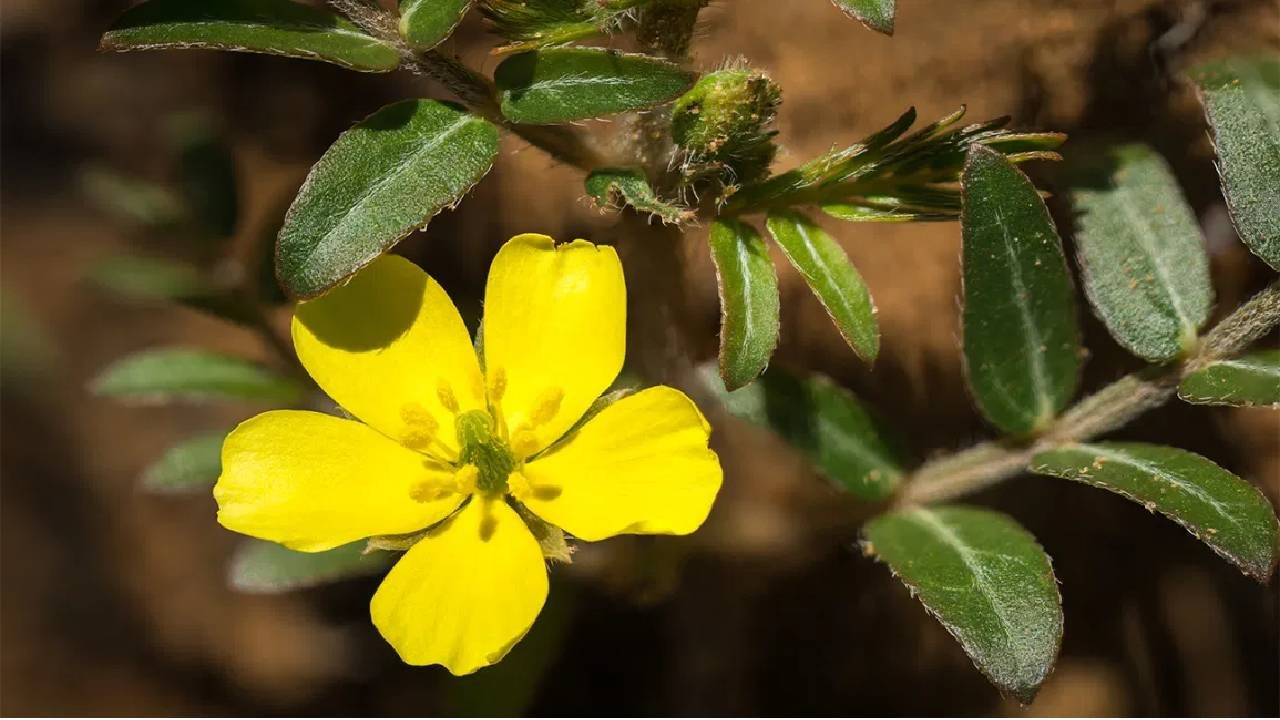
Puncture vine, commonly known as goat head or Tribulus Terrestris, is indeed a warm-season annual endemic to southern Europe’s Mediterranean area. It was accidentally brought to North America by early European immigrants whenever the plant’s blasted burs crept their way across the Atlantic in sheep wool. Because of the hitchhiking ability of its seeds, the puncture vine had already spread rapidly over the continent since then.
Puncture vine does have a prostrate growth habit, which means that its tendrils lie flat on the ground and extend outward from a central point. It only grows vertically when it is shaded or squeezed out. Its leaves are split into multiple tiny leaflets, and its blooms have five petals and are petite and bright yellow. It’s a lovely shrub except for the menacing, jagged fruits that appear after the blossoms. Since these fruits dry, they fall from the plant, break into five pieces, and are ready to puncture your tire, find their way further into the bottom of your shoe or even the foot of an animal, or cling onto some stray hair.
Depending on the circumstances, puncture vine can remain relatively tiny or spread up to six feet wide. Fruits begin to develop immediately after blooming, and seeds mature shortly thereafter, so if the plant is not removed swiftly – nutlets and all – successive populations are ensured. Fortunately, the plants are rather simple to remove. They pull up readily unless the earth is especially compact, and if they split off at the root, they normally do not sprout again.
At first sight, almost any plant with prostrate growing conditions and that is continuously expanding in the summer might be mistaken for a punctured vine. A closer look will assist to confirm the plant’s genuine identification. Purslane, as well as spotted spurge, are two plants that may mislead you. Both of the above species can be seen growing along with puncture vine in full sun in disturbed or abandoned areas.
Habitats
Puncture vine thrives in pastures, cultivated fields, sides of roads, pavements, parks, as well as waste places and is most commonly found on sandy, dry, or gravelly soils.
Impacts
Puncture vine generates highly pointed burs that irritate bare feet as well as cause bicycle flats, decreasing recreational use in many places. Seeds may damage even light vehicle tires. Puncturevine has a strong taproot and may compete fiercely in agricultural regions for both nutrients and water. Puncturevine’s sharp spines can injure livestock’s mouths, digestive systems, and feet.
Ecology and biology
Puncturevine reproduces alone by seed. A single plant may yield up to 400 fruits, each bearing two to three seeds. Germination often begins in the spring as well as continues until frost. Puncturevine requires a high temperature to germinate and develop. Burs split as they grow and might spend years in the soil until germinating. Puncturevine grows best in light-textured soils, although it will grow in practically any soil. From June through September, the plant blooms. Puncturevine grows in mats with stems that are 3 to 5 feet in diameter. Puncturevine has a basic taproot as its root system.
Management Methodologies
To manage puncture vine, chemical, mechanical, as well as biological control methods are available. Long-term preservation as an annual is best done by employing management strategies before seedset.
Control of Puncture vine:
Reduce the number of seeds in the soil to ensure that this plant does not regrow as heavily as it did the previous year. This can be achieved by removing the crop before it has a chance to generate seeds or blooms in March. Puncturevine does not vanish; for complete eradication, you must continue to remove the plant for several years.
- Cultural Command
Pulling Puncturevine out by hand is a smart technique to deal with it. Wear gloves if you opt to control the weed in this manner to protect one’s hands from the thorny burs. Hoeing Puncturevine is another effective way to cut the plant’s root system. Make certain that all stray burs are managed to pick up while removing this plant. Because the burs are the plant’s seeds, this is a key step in culturally managing this plant. Keeping a watch on the area where you eliminate the weed in the spring and early summer, and plucking off Puncturevine if it decides to sprout, can drastically restrict growth for the next year. In gardens, screening off light with 3-inch thick mulch is also beneficial. Puncturevine, on the other hand, may regrow if the specimens fall on mulch. Planting a competing, attractive plant in the area in which the weed used to grow or may grow in the future will diminish the weed’s resources.
If used when the plant is still tiny and/or immature, chemical control herbicides can be an effective technique to manage Puncturevine. Products containing 2,4-D, dicamba, or glyphosate may be beneficial against this weed. 2,4-D and dicamba are safe to use on lawns and will not harm the desired grass. It’s indeed, however, harmful to broadleaf plants. The easiest strategy to control the spread of this plant is to spray the pesticide near the weed while there is little to no wind to reduce drift. Glyphosate herbicides are toxic to all plants and should only be employed for spot treatment.
- Biological Management
In the United States, two biological warfare agents have indeed been released. A seed-eating weevil (Microlarinus lareynii) sucks on seeds as a larva as well as pupates in them, damaging them. A stem and root crown-mining beetle (Microlarinus lypriformis) with larvae that burrow into stems as well as root crowns is the second agent.
Health Benefits :
Tribulus is generally utilized as a sexual health supplement. Furostanol saponins are naturally occurring steroidal chemicals in Tribulus that enhance testosterone (male sex hormone) synthesis by suppressing natural hormone receptors. This causes an increase in the production of luteinizing hormone (LH), which stimulates the Leydig cells throughout the testes to create more testosterone.
A Tribulus Terrestris pill gives males with low testosterone an instant boost. According to one study, it can produce an increase in sperm concentration. It may also give long-term prostate support for a guy as he ages. In any case, it provides men with natural ways to maintain testosterone levels as well as physical, mental, and sexual wellness. Because testosterone is involved in the production of athletic traits such as energy vigor, muscle strength, and aggression, athletes frequently utilize Puncture Vine supplements to increase their performance.
Tribulus is also recognized to help women’s sexual function. Women who drank Tribulus had higher levels of sexual yearning, arousal, and fulfillment than those who did not. Several studies have linked Tribulus supplementation to hormone homeostasis in the body.
Herb extracts are occasionally used orally and topically to treat skin disorders such as allergens, eczema, scabies, as well as psoriasis. Tribulus has been shown to successfully decrease redness and skin sores in leprosy patients.
Puncture Vine may be beneficial in alleviating angina or chest discomfort symptoms. According to the preliminary clinical study, Tribulus may have antianginal action. It appears to dilate coronary arteries, hence improving coronary circulation. Tribulus is also used to treat anemia on occasion.
Puncture Vine improves digestive system function in a variety of ways. Tribulus is used as a mild laxative in Unani medicine. Some study suggests that saponins can be utilized to treat smooth muscle spasms and colic discomfort. It increases appetite and decrease the lipid level. It relieves intestinal gas and helps to remove intestinal parasitic worms.
Tribulus appears to help with milk flow during nursing, according to limited research. It makes labor easier by toning the smooth muscles in the region. The effectiveness of Puncture Vine in labor is currently under investigation. Some studies also suggest that it may be a cause of miscarriage, thus pregnant women should be using Puncture Vine with caution. Treats Infertility
Several research studies have consistently shown that taking the extract regularly enhances ovulation in women with irregular ovulation patterns. Tribulus also helped restore normal ovular function and decreased the number of cysts in women having Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS).
Tribulus Terrestris supplements have been prescribed to treat hypertension. Repeated rat studies reveal that when aqueous extracts of the plant were given to hypertensive rats, their blood pressure was indeed reduced. Furthermore, the treated rats had considerably reduced angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) activity than just the untreated rats.
Other Advantages
Extracts from either the fruit or leaves appear to have diuretic properties, which may explain why Tribulus has traditionally been used to treat kidney stones as well as other urinary disorders such as unpleasant urination. As a result, Tribulus is frequently referred to as a water pill. Tribulus is used by a small number of people to treat headaches, gonorrhea, liver illness (hepatitis), inflammation, coughs, chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS), chronic stiffness (rheumatism), and dizziness (vertigo). It also functions as a tonic and is said to have mood-enhancing properties. Tribulus is a plant that has been shown to improve mood, stress, as well as anxiety. This might be beneficial for women who have several duties or are dealing with premenstrual syndrome symptoms (PMS).
Warnings And Special Precautions:
Breast-feeding and pregnancy: Taking Puncture Vine when pregnant is POSSIBLY DANGEROUS. According to animal studies, Tribulus may be harmful to embryonic development. There is not enough information available concerning the safety of using the Puncture Vine when breastfeeding. If you are pregnant or breastfeeding, avoid using Tribulus. Puncture Vine may aggravate prostate disorders such as benign prostatic hypertrophy (BPH) or prostate cancer, according to research. According to new research, Tribulus can enhance prostate weight.
Diabetes. Tribulus may lower blood sugar levels. Your diabetic medication dosage may need to be modified by your doctor.
Surgery: Tribulus may affect blood sugar levels. This may impair blood sugar management both before and after surgery. Stop taking Puncture Vine at least two weeks before your procedure.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
When used by mouth for a short length of time, Tribulus supplements are POSSIBLY SAFE for most people. They have been employed safely in up to 8-week research investigations. Tribulus’ long-term safety is uncertain. It is LIKELY UNSAFE to consume the spine-covered fruit of Puncture Vine. A major lung condition has been connected to eating the fruit, according to reports.
DOSING
The proper Puncture Vine dosage is determined by numerous factors, including the user’s age, illness, and other circumstances. There is currently insufficient scientific evidence to define a suitable range of Puncture Vine dosages. Keep in mind that organic ingredients are not always safe, and doses might be critical. Before using, be sure to read the product label as well as consult your pharmacist, physician, or another healthcare expert.
Interactions
There appear to be no interactions between Tribulus and meals, plants, or supplements. If you use diabetic medication, Puncture Vine may cause dangerously low blood sugar levels. It may also boost the impact of steroids on your body. Inform your physician about any supplements you’re taking, regardless of whether they’re natural.
FAQs:
Animal studies have indicated that Puncture Vine helps reduce blood sugar levels and, as a result, might be utilized as a medicine for diabetes mellitus.
One of the primary causes of male infertility is erectile dysfunction, which is associated with low concentrations of Dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA). Protodioscin, a Puncture Vine component, is responsible for increasing DHEA levels in the male system. It also boosts sperm concentration and motility.
Conclusion:
Thus after consulting doctor you can take puncture vine. It is used for kidney issues, which includes kidney stones, difficult to urinate, a kidney problem called Bright’s infection, and as a “water pill” to increment in urination. For skin issues, including psoriasis, scabies and dermatitis (atopic dermatitis) it is very helpful.